ACCESS
The foremost challenge for Universalisation of Elementary Education is the enrolment & retention of all children of age group 6-14 years in schools. In spite of huge expansion of schooling in formal and non-formal system a good number of children in age group of 6-14 years are yet out of school.
Universalization of Elementary Education is primarily depends on Access and retention.
OPENING OF NEW SCHOOLS:
State Norm for Opening of New Primary school:
Govt. in School & Mass Education Deptt. vide Notification No.19917, dt.22.08.13 has notified that : Section-2 (f) of Right of Children to Free & Compulsory Education Act, 2009 stipulates that “elementary education shall mean the education from first class to eighth class”.
Pursuant to the above provisions of the Act, it has been decided that:- Primary Schools means the schools having classes I to V and Upper Primary Schools means the schools having classes upto VIII for all purposes.
Govt. Upper Primary schools have been upgraded to Class-VIII accordingly.
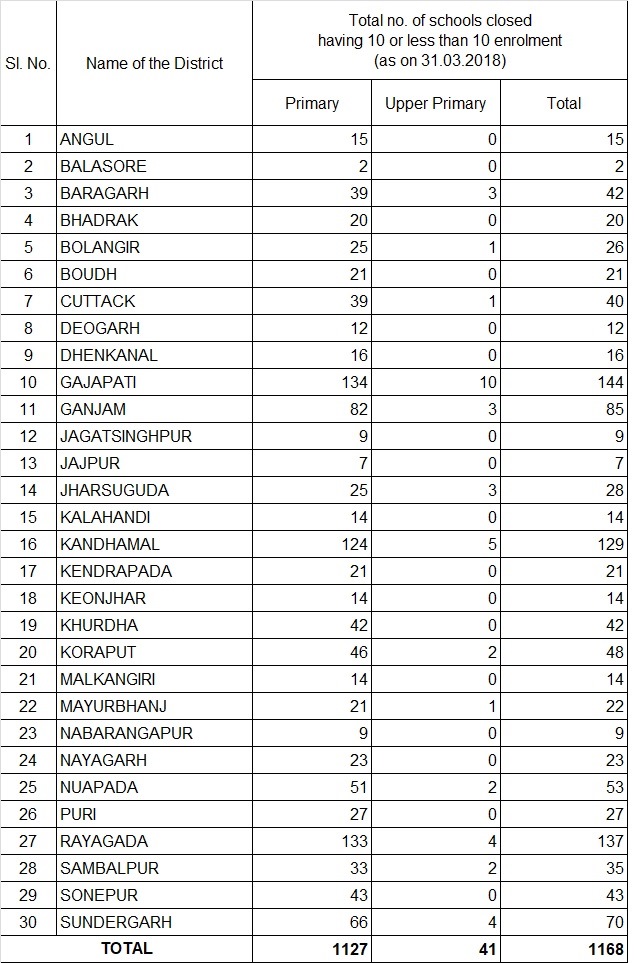
MERGER / CLOSURE OF SCHOOLS:
The Government in School & Mass Education Department vide letter No. 12171/SME, dt.23.06.2016 have been pleased to pass order for merger/closure of non-optimal schools having 10 or less than 10 enrolments with nearby schools subject to the following conditions.
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
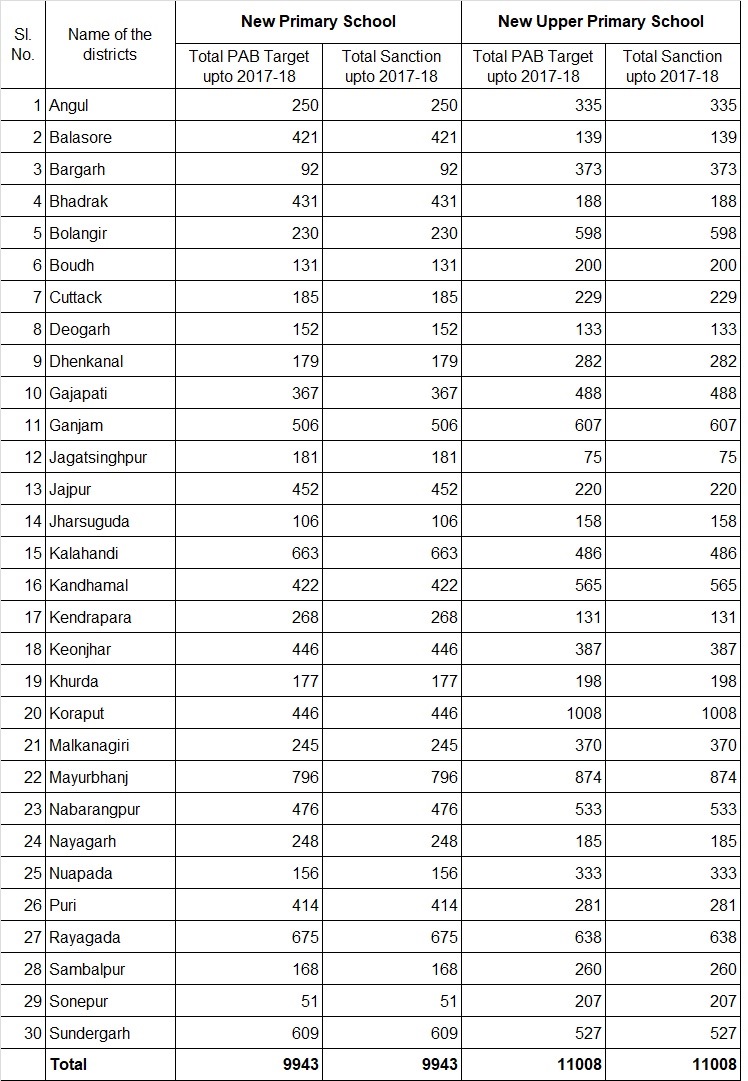
TARGET & SANCTION OF NEW PRIMARY SCHOOL UNDER SSA UP TO 2017-18
STATUS OF CLOSURE / MERGER OF SCHOOLS UPTO 2017-18
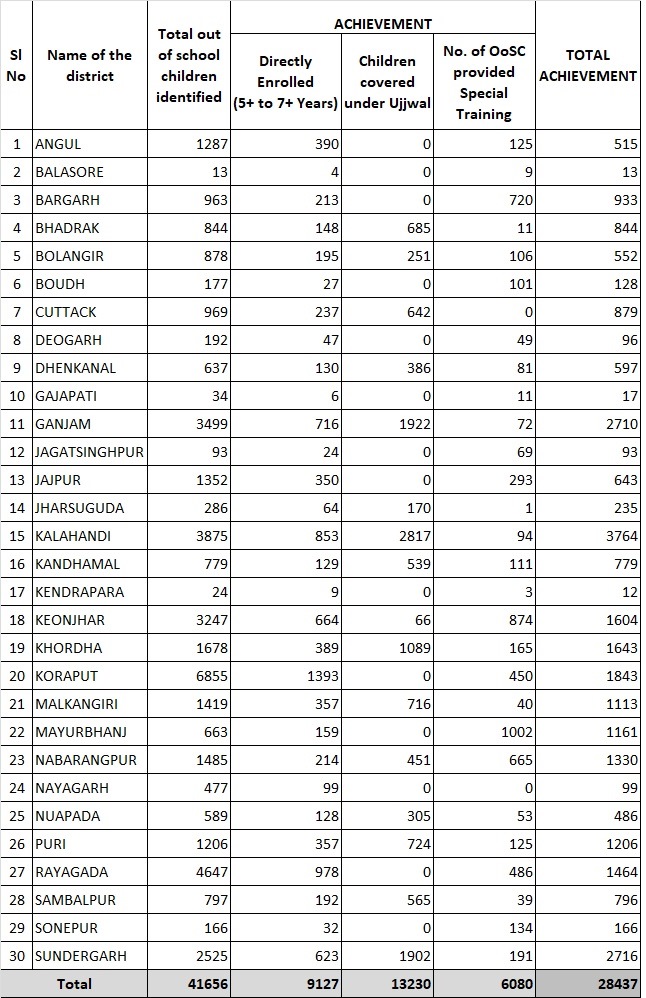
SPECIAL TRAINING TO OUT OF SCHOOL CHILDREN: 2017-18
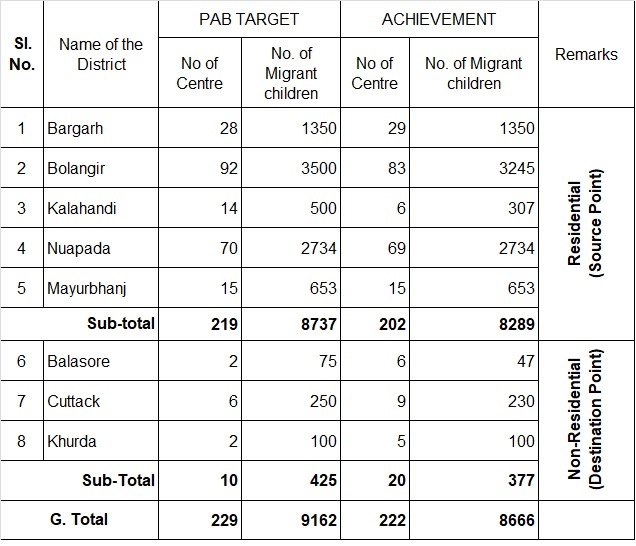
SEASONAL HOSTEL : 2017-18
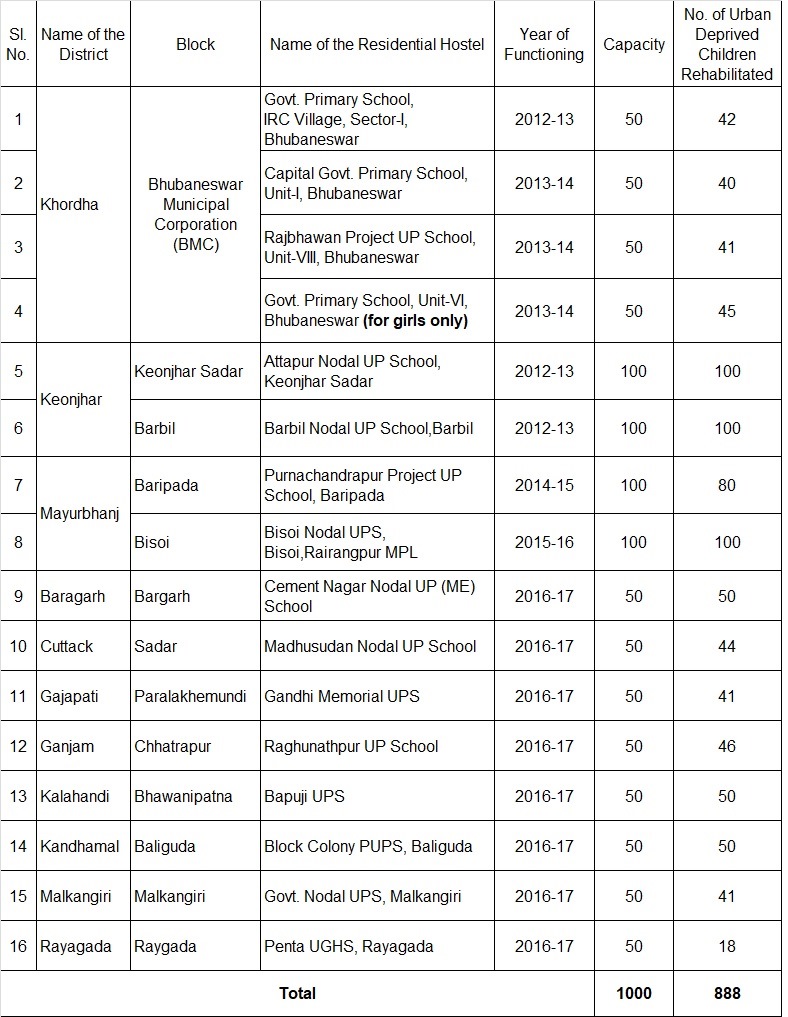
RESIDENTIAL HOSTEL : 2017-18
(for Urban Deprived Children)
TRANSPORT AND ESCORT FACILITIES: 2017-18
Community Mobilisation
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is an effort to universalize elementary education with the active involvement of community. It is also an attempt to provide an
Community Mobilisation Active involvement of Community plays a critical role in meeting the access – equity – quality mandates of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) in the context of Right to Education (RtE) Act 2009. With the participation of the community in the management of schools social, regional and gender gaps can also be bridged. It is essential that people are well aware about their role and responsibilities as parents, guardians, members of local authorities and they are given freedom for the development of the school. The state has always encouraged school teachers to understand the role and importance of community participation, contribution in development of school and quality enhancement. For this constant focus on active community participation through various initiatives has been given priority Suravi : State-level children’s festival is being organized on the eve of Children’s Day This programme educates, entertains and inspires young minds from across the State in the city of Bhubaneswar. The event has turned out to be a platform for budding talents of the State’s far-flung areas. Children enjoy a huge range of workshops, competitions, cultural programmes, musical performances and exhibitions. This programme is being organized at Cluster, Block, District and State level.
Street Play : Street play is a form of theatrical performance and presentation in outdoor public spaces without a specific paying audience. It aims at creating awareness among the public about educational rights and their importance. People watch the plays with rapt attention, soaking in everything that was being told to them through this medium. RtE Awareness : To ensure proper implementation of the Right to Education (RTE) Act-2009 and RCFCE Rule 2010 various initiatives have already been taken at State level. The main objective of the campaign is to create awareness among the masses regarding benefits provided to poor people, weaker sections and disadvantaged groups, under Right to Education (RTE) Act 2009, especially regarding 25% free seats (pre-school or 1st std) reserved for them in private schools. Shiksha Mahasabha/ Parental Counseling : Shiksha Mahasabha is being organised particularly in Tribal Sub Plan (TSP) areas and SC concentrated panchayats to mobilize the community towards the fundamental rights, provisions, facilities available and benefits of education and also mobilize them in ensuring enrollment and regular attendance of their wards at school. Parental counselling helps parents to know new ways to understand themselves as parents, develop more trusting and secure relationships with their children, assist their children to cope with the challenges of growing up. Community Based Activities for School Community Linkage : Community based activities are the activities or programme where teachers act as facilitators and provide space for the community and children to take part in creative activities like exhibition of art and handicraft, traditional musical instruments, ornaments, dance, cultural songs, riddles, tales etc. Special focused districts : There are 18 Special Focus Districts in Odisha. Community based child centered activities are being organised for overcoming specific gaps in overall endeavour of the districts to achieve universal elementary education.
EDUCATIONAL PLANNING UNDER RTE-SSA, ODISHA
Planning is a tool as well as a process for creating platform, indicates direction and provides solution for educational interventions in the field of infrastructure, access, socio-gender equity, quality and educational management for achieving UEE under the RTE Act, 2009 with the given objectives, resources and time. It also encourages creativity and innovation

INCLUSIVE EDUCATION
Inclusive education is about all children learning together even if they differ from each other in styles and place of learning.
Inclusive Education for the Children with Special Needs under Samagra Shiksha
The Integrated Scheme on School Education aims to look at education of all children including children with Special Needs (CwSN) in a continuum from pre nursery to class XII. The scheme will cover all children with special needs with one or more disabilities as mentioned in the schedule of disabilities of the Right of the Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016 studying in Government, Government-aided and local body schools.
The scheme stresses on working in convergence with all the line Departments/ Ministries and intends to provide relevant holistic support for effective and appropriate services.
The objectives of the scheme are:
Identification of children with disabilities at the school level and assessment of her/his educational needs.
Provision of aids and appliances, assistive devices, to the children with special needs as per requirement.
Removal of architectural barriers in schools so that students with disability have access to classrooms, laboratories, libraries and toilets in the school.
Supplying appropriate teaching learning materials, vocational training support, guidance and counseling services and therapeutic services to children with special needs as per his/her requirement in convergence with line departments.
General school teachers will be sensitized and trained to teach and involve children with special needs in the general classroom. For existing special educators, capacity building programmes will be undertaken.
CwSN will have access to support services through special educators, establishment of resource rooms, vocational education, therapeutic services and counseling.
Target Group
The scheme will cover all children from pre nursery to senior secondary stage studying in Government, local body and Government-aided schools, with one or more disabilities as defined under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act 2016 namely:
1. Blindness
2. Low-vision
3. Leprosy Cured persons
4. Hearing Impairment (deaf and hard of hearing)
5. Locomotor Disability
6. Dwarfism
7. Intellectual Disability
8. Mental Illness
9. Autism Spectrum Disorder
10. Cerebral Palsy
11. Muscular Dystrophy
12. Chronic Neurological conditions
13. Specific Learning Disabilities
14. Multiple Sclerosis
15. Speech and Language disability
16. Thalassemia
17. Hemophilia
18. Sickle Cell disease
19. Multiple Disabilities including deaf blindness
20. Acid Attack victim
21. Parkinson's disease
Girls with disabilities will receive special focus and efforts would be made under the scheme to help them gain access to schools, as also to provide motivation and guidance for developing their potential.
The UDISE will have the relevant details of children. Further an extensive database will be maintained at district and block level which will cover all the particulars of children including the type of disability, degree of severity, educational needs, emergency contacts and all other relevant details that will help the district, block level management to cater to the needs of the CWSN.
Components of the Scheme
The Scheme will include assistance for two kinds of components:
Student oriented components
The student oriented component may be utilized for specified items like:-
INFRASTRUCTURE FACILITY
The role of Civil Works in Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan in the light of RTE is to provide physical infrastructures as per the need throughout the State to achieve the basic objectives of RTE i.e. Universalisation of Elementary Education with a prime goal of establishing a sustainable system
The role of Civil Works in Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan in the light of RTE is to provide physical infrastructures as per the need throughout the State to achieve the basic objectives of RTE i.e. Universalisation of Elementary Education with a prime goal of establishing a sustainable system. Execution through SMC / SMDC with active participation of local community rather than through any other agency is the salient feature of SSA Civil Work & opens up the vista for achieving sustainable Elementary & Secondary Education in the State. Needless to say that appropriate planning is being constantly taking place to address many issues coming up while implementing the project. The issues are analyzing at the grass root level, need based assessment studies, prioritization, mobilization of funds and its utilization for the essential activity in the right time from the limited available funds, exploring possible resources from other department to give a complete realistic shape to the project as much as possible. It is worthwhile to mention here that sister Project such as Kasturaba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV), of course with the same objective & goal, have gone a long way in supplementing the Programme for the main stream. The project aims not only in creating infrastructures like new schools or addl. class rooms but also providing the basic requirement like separate toilets for Girls & Boys, drinking water facilities etc. so as to increase the access and reduce the dropout rates in Elementary & Secondary Schools. Special attention for the CWSN is also part of planning process.
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM (MIS)
MIS plays a key role in the SSA to support the management for decision making by providing the right information in right time
MIS plays a key role in the SSA to support the management for decision making by providing the right information in right time. It is first amongst the Govt. sector projects in India that is being so closely monitored through a Management Information System. Various data are being collected, computerised and compiled in a system for effective planning and progress monitoring. The MIS units at State Project Office, 30 District the inception of the Project and equipped with necessary infrastructure and personnel. Broadband Internet connectivity has been provided to each location.
SCHOOL STUDENT HELPLINE (SSH)
School Student Helpline is a unique initiative of the S & ME department of Odisha, set up at OPEPA for ensuring the Right of Children to free and Compulsory Education Act 2009
Introduction:
School Student Helpline is a unique initiative of the S & ME department of Odisha, set up at OPEPA for ensuring the Right of Children to free and Compulsory Education Act 2009. It began as a channel of communication between school students (I-X) and the Department in the year 2010. It has a toll free phone number (18003456722) through which any child whose right to education is at stake can draw the attention of the apex authorities. It functions on all working days from 8 A.M to 8 P.M
About 53 category of cases registered such as Children entitlements, child abuse ,Infrastructure related , Sanitation related ( Drinking water, toilet ),Misuse of school building/ premises, Teacher related (absenteeism , negligence in duty, shortage of teachers, Private tuition, Mid-Day Meal, Financial irregularities, School Management Committee ( Formation & conflict resolution) ,Admission related CWSN, Social issues-caste. The graphical presentation of the major RTE related cases is given below:
Operational Strategy:
Major RTE cases Received by end of 2017

Number of activities were undertaken to strengthen the system:
1.Capacity Building programme on functioning of SSH:
COMPUTER AIDED LEARNING PROGRAMME (CAL)
Technology has become an increasingly influential factor in education today
INTRODUCTION
Technology has become an increasingly influential factor in education today. Computers and mobile phones are used in developed countries for improvement in education practice and to develop new ways of learning. Technology provides powerful learning tools and provides new ways to engage students in the schools. Computer Aided Learning (CAL) Programme in elementary schools has been introduced with the aim to develop the learning capacity of the students and increase the teaching productivity and effectiveness of instructors with the help of advance Computer based Technology. With the normal teaching method, students would feel uninteresting and easily forget what teachers have taught. This system adopts the newest Computer Technology, illustrating with the attractive pictures & animations, playing with music & voice. The students will feel happy & willing to study consciously. Besides, the students would also be proud to show others that they are able to use Computer. Computer Aided Learning in Upper Primary Schools does not aim at teaching intricacies and technicality of computers. It aims at providing joyful, interactive and interesting ways of learning, through illustrations, examples and interactive tools particularly designed to emphasize on the HARDSPOTS of the regular curriculum.
OBJECTIVES
COVERAGE
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
KASTURBA GANDHI BALIKA VIDYALAYA
182 nos of KGBVs are functional in Odisha
The Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV) scheme was launched by the Government of India in August, 2004 for setting up residential schools at upper primary level for girls belonging predominantly to the SC, ST, OBC and minorities in difficult areas. The scheme of the KGBV run as a separate scheme but in harmony with the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), National Programme for Education of Girls at Elementary Level (NPEGEL), .from 1st April, 2007 it has merged with the SSA programme as a separate component of that programme. A socially conscious and literate society has a vital role to play in democracy. Eradication of illiteracy has been one of the major national concerns of the government of India since independence. To address the issues of gross girls drop out in upper primary school, gender disparity and regional disparity in literacy especially for girls belonging to SC,ST,OBC and minority in educationally backward blocks where female literacy is below the national average and gender gap in literacy is more than the national average."Kasturaba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya" is a programme basically meant for educational development of girls at upper primary level. The objective of KGBV is to ensure access and quality education to the girls of disadvantaged groups of society by setting up residential schools with boarding lodging facilities at elementary level.
182 no. of KGBVs are now functioning in 23 Districts of Odisha under Model-III. The no of KGBVs sanctioned phase wise are 49, 65, 43&25 in 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th phase respectively. In 82no.of KGBVs where the boarders strength have been increased to 150 in the year 2018-19,the other 100 KGBVs were functioning with the strength of 100 which will be upgraded to 150 in the year 2019-20.
| Sl No | Name of the District | No. of KGBVs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| @100 Strength | @150 strength | Total | ||
| 1 | Angul | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 2 | Balasore | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 3 | Baragada | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| 4 | Bhadrak | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | Bolangir | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 6 | Boudh | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 7 | Deogarh | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 8 | Dhenkanal | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | Gajapati | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| 10 | Ganjam | 17 | 0 | 17 |
| 11 | Jajpur | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 12 | Kalahandi | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 13 | Kandhamal | 3 | 8 | 11 |
| 14 | Keonjhar | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 15 | Koraput | 1 | 13 | 14 |
| 16 | Malkangiri | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| 17 | Mayurbhanj | 26 | 0 | 26 |
| 18 | Nabarangpur | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| 19 | Nuapada | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 20 | Rayagada | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 21 | Sambalpur | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 22 | Subarnapur | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| 23 | Sundergarh | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| Total | 100 | 82 | 182 | |
Total number of KGBVs sanctioned for the state of Odisha is 182. Out of which 182nos. of building has been completed in all respect.


All 182 schools having KGBVs have been constructed boundary wall for ensuring safety environment to the children; Schools/KGBVs have been well protected with Boundary wall. Besides as additional safety measure, steps have been taken to construct high height boundary wall in convergence with District Administration.

Each KGBV has been provided with good no of Toilet. As all the KGBVs are functioning in Model-III approach, for providing better facility Girls Toilet have been constructed in each school campus. Steps have been taken for the construction of Incinerators in all the 182 nos. of KGBV
School having KGBV are provided with different furniture like Almirah & Selves for safe storage of records, Table & chair, Cot for the inmates, Television, Music System, Water Purifier, Paper stand, shoe stand has been provided for ensuring standard living condition to the inmates. Besides, the facility of gas connection, cooler, refrigerator, water purifier, have been provided in all the KGBVs respectively through convergence.
Indoor and outdoor games play a vital role in developing the physical health as well as personality of the child. The Part time teacher, warden and Gender Coordinators of all the 182 KGBVs have been trained at State level. Accordingly, the KGBVs have instructed to purchase all required sports materials for the boarders.


All KGBVs are provided with beddings like mattress, bed sheet, pillow, blanket, mosquito net etc. Replacement of bedding fund have been utilised in38 nos. of KGBVs. Besides, medicated mosquito net has been provided to all the inmates in convergence with NRHM.
The KGBVs running in Govt. accommodation have been electrified and have good water facilities except few. The completed building have equipped with electrification and water facilities with overhead tank, water connection to toilet and bathrooms etc. have been made in convergence with RWSS & Electricity department.
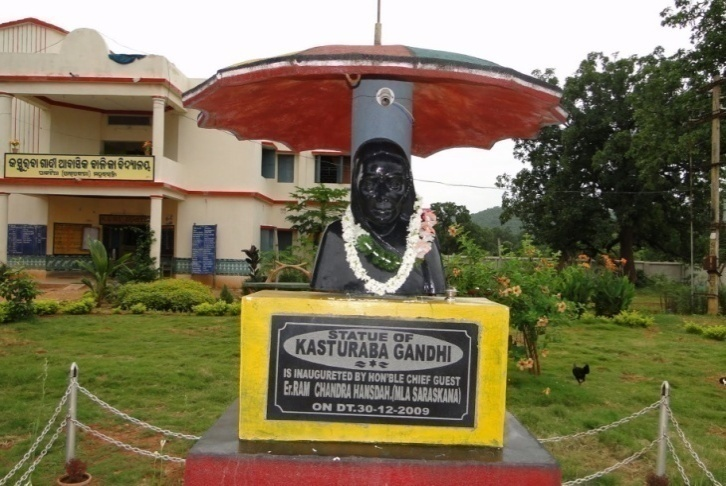
To create a healthy environment & to develop a positive attitude, Child Friendly Environment like flower Garden, kitchen garden has been created with proper drainage system in different KGBVs. A Statue of Kasturba Gandhi has been established in the campus. Ramps have been constructed to create a barrier free environment for the CWSN in the school & hostel campus. Watch post/Watch rooms have been constructed in KGBVs in convergence with District Administration & CSR fund. One Resource Room has been developed for the inmates to exhibit the art craft & vocational items. All KGBV schools have been covered under Computer Aided Learning.



Towards maintenance of girls in KGBV Rs. 1500/- per month per girl have been provided & steps taken for providing qualitative nutritious food with hygienic condition. District specific Food Menu has been prepared through a district level committee by involving Nutritionist. Steps taken to provide Cooking Gas to each KGBV. In order to maintain the prescribed food menu a Food Committee has been formed at KGBV level by involving the inmates of the girl who will supervise& ensure the preparation of food as per the menu. Govt. has taken steps to provide subsidized rice @ Rs.1 to the inmates through Food & Civil Supply Dept. 23 no of KGBV districts have already been availed the subsidized rice for the inmates. The child Cabinet has been formed by taking the inmates& Food Minister has been nominated to ensure the preparation of food, in hygienic condition. Girls have been oriented on hygienic practice, hand wash before taking meals etc. Utensils have been properly cleaned by the Cook, Asst. Cook etc. & Tray and other utensils of inmates have been properly cleaned with washing powder & hot water etc. in weekly basis.

| Days | Breakfast (6.30-7.AM) (300 Cal Approx.) and one fruit daily | Prelaunch (9AM-9.30AM) (Approx. 400Cal) | Lunch (1.30-2.00PM) (Approx.800 Cal) | Evening Refreshment (5.30-6.00PM) (Approx.300 Cal) | Dinner (9PM-9.30PM) (700 Cal) Followed by 1cup milk-75ml |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunday | 6 pcs of Biscuits- 30g | Idli 6 pc (100g) &Coconut+BadamChatani (20 g) | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Mutton-50g(NV)/Paneer or Mushroom-50g for veg. | Chat (Boiled Matar, potato, onion, papad, Badam)- 100g | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Dalma-25-30g, Salad-20g, Papad-1pcs,Pickle-5g |
| Monday | Chuda-50g, Sugar-10g, Banana-1p, Coconut-10g- Total-100g | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Spinach- 50g , Egg curry-50g (NV) / Mix veg curry-50g (V) | MDM (Rice +Dalma) | Green leaf mixed Pokodi-100g | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Tadka-50g, Aludam- 50g |
| Tuesday | SujiHalwa/ Suji Upama-100g | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Mix veg Fry-50g, Small Fish Curry or prawn curry(NV)/Mushroom curry-50g (V) | MDM (Rice + Soya curry) | (Chhuda, Badam, Rasi, Jaggary)- Laddu-2pcs 50g each | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Dal-25-30g, Mixed veg curry-50g, Pickle-5g |
| Wednesday | ChudaUpama- 100g | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Spinach- 50g , Mixed veg fry-50g, salad-50g | MDM (Rice + Egg curry) | Mudhi Mixture-100g | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Chicken curry-50g (NV) /Chhole ( Kabuli Chana) curry-50g (V), Papad-1pcs,Pickle-5g |
| Thursday | Sprouted Green Gram (GajaMung)+ Jaggary- 100g | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Spinach- 50g , Egg curry-50g/ Mix veg curry-50g, Salad-50g | MDM (Rice +Dalma) | Mixed Veg Upama-100g | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Soyabean curry-50g, Tomato khata-50g |
| Friday | Semia, Khiri/ Upama-100g | Rice- 100-150g, Dalma-25-30g, Spinach- 50g , Bhaja-50g, Fish curry-50g (NV) /Paneer masala-50g (V) | MDM (Rice + Soya curry) | Seasonal ripe fruits-(2-3 pcs) | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Rajma curry-50g, Mixed veg fry-50g |
| Saturday | Bread Jam- 100g | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Spinach- 50g , Mixed veg Curry-50g | MDM (Rice + Egg curry) | Boiled chhana, onion- 100g | Rice- 100-150g/ Roti-2-3pcs, Mixed Veg Santula-50g, Chips-10g |
| Holiday | 6 pcs of Biscuits- 30g | Puri-4pcs, Alu curry-50g,Sweets-1p | Rice- 100-150g, Dal-25-30g, Fish Curry-50g (NV)/Mix veg-50g (V), Ambila-50g, Papad-1pc. | Mudhi Mixture-100g | Veg Palau-100g, Santula-50g, Pickles-5g |
| N.B.-A. The time of Lunch for Sunday, Saturday, Holidays and morning schools will be 1 PM to 1.30 PM | Calorific value of the Items: Per 100g) | ||||
| B. Recommendation of ICMR (overleaf) must be referred. | Rice-117-200Cal,Roti-106Cal (medium), | ||||
| C. Always fresh and leafy vegetable will be given | Dal: 360Cal, Ground nut- 567 Cal,Spinach-23Cal | ||||
| D. At any cost spoiled/ rotten/ stale and unhygienic food will not be permitted | Mutton: 234Cal, Chicken: 175 Cal,Fish-87 Cal | ||||
| E. Iodised Salt always to be used in recipes. | prawn-105 Cal, Chuda-105Cal, Potato-77Cal | ||||
| F. Tube well water/boiled water/ water from purifier can be used as drinking water. | Mushroom-38 Cal, Panner-72 Cal, Milk-160 Cal | ||||
| G. Hand washing practices and personal hygiene must be monitored. | Coconut- 444Cal, Egg-173Cal, Suji- 348Cal | ||||
The following instruction has been given to KGBV to adhere strictly:
Free Text Books have been provided to all girls. Besides they have been provided with class wise subject specific supplementary reading writing materials like Note book, Hand Writing Copy, Translation Book & copy, Drawing Copy, drawing materials, Geometry Box, materials for Science & social project, Essay Book, Dictionary, Word Book etc. Further Math & Science Kit has been provided to each KGBV in convergence with NCERT to give the children better exposure in science and Math. Remedial classes are being taken by the part time teacher to provide additional educational support to the slow achiever.


MORNING NEWSPAPER READING BY THE STUDENTSUSE OF HOSTEL LIBRARY
Stipend to disadvantaged/ weaker section girls @ Rs. 100/- per month per child is being deposited in the Savings Account of girl inmates to provide educational incentives .
For enhancement of self confidence among the girls and to enable them to face the challenges they come across in their day to day life they have been trained in different skills like art & craft, computer, Tailoring, Song, Dance, Wool Knitting, Phenyl, preparation, making of greetings, Teddy Work, Bamboo Work, Clay Model, Candle Preparation, Incense Stick Making etc., training on sport activities, exposure to different systems such as Banking system, Service of Police, Postal etc. As they are the creator of the future society steps has been taken to create awareness among them on different social issues like child marriage, dowry system, female feticide, adolescent issue etc. through different awareness programmes at KGBV level.


VOCATIONAL TRAININGVOCATIONAL TRAINING
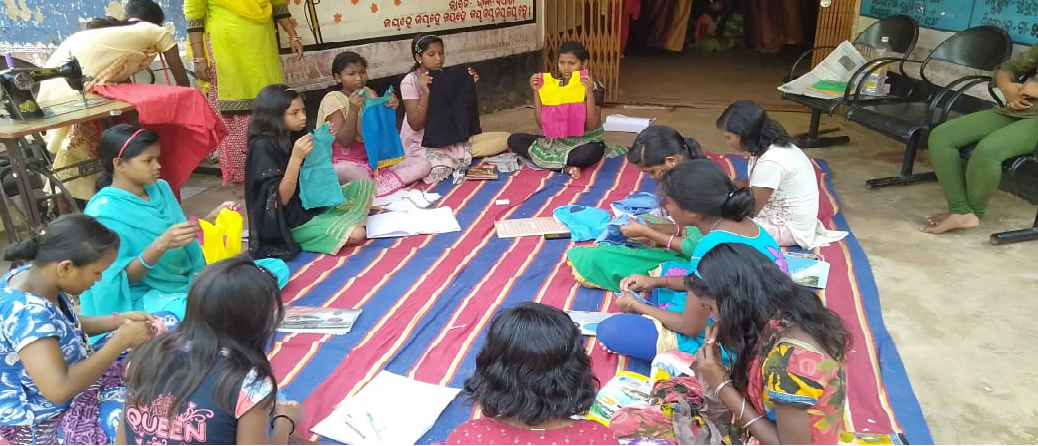
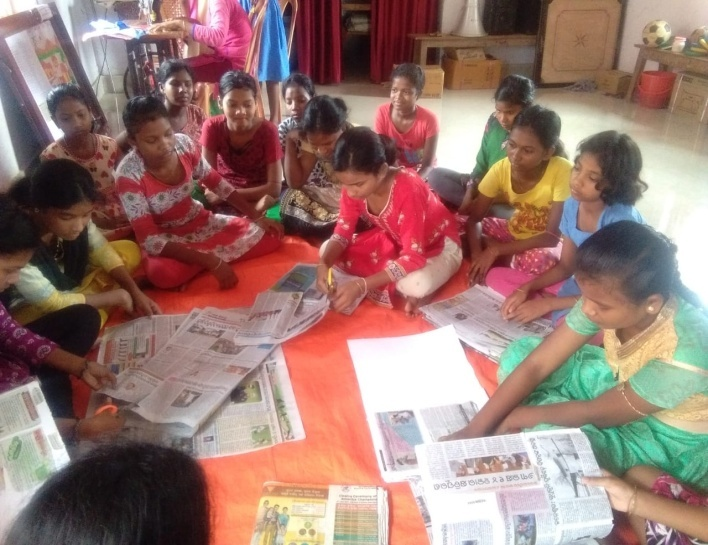


VOCATIONAL TRAININGORIGAMY PREPARATION BY THE STUDENTS
For providing better exposure & enhancement of skills of staff different Training & workshop has been organized at KGBV/District/Zonal& State level. All staff like Head Teacher, one Asst. Teacher from School, 3 Part Time Teachers, Accountant, & Warden has been oriented on Hostel Management. Part Time Teachers have been oriented on physical education. The District has also organised different trainings for Wardens on safety & security issues in convergence with Women & Child Development Deptt. & conducted training of Part time Teachers on Bridge Course & Remediation in convergence with DIET.
182 nos of Part Time Teachers have been imparted training on Learning Enhancement programme under on-going UTTHAN at State level.
All the KGBVs have been electrified for creating a safe and secured environment. Besides, all the rooms of both school & hostel have been well lighted. Provision of fan, water pump, solar light, inverter etc. have been ensured. Running water facility has been provided in convergence with RWSS. Tube well and well are also available in the campus.

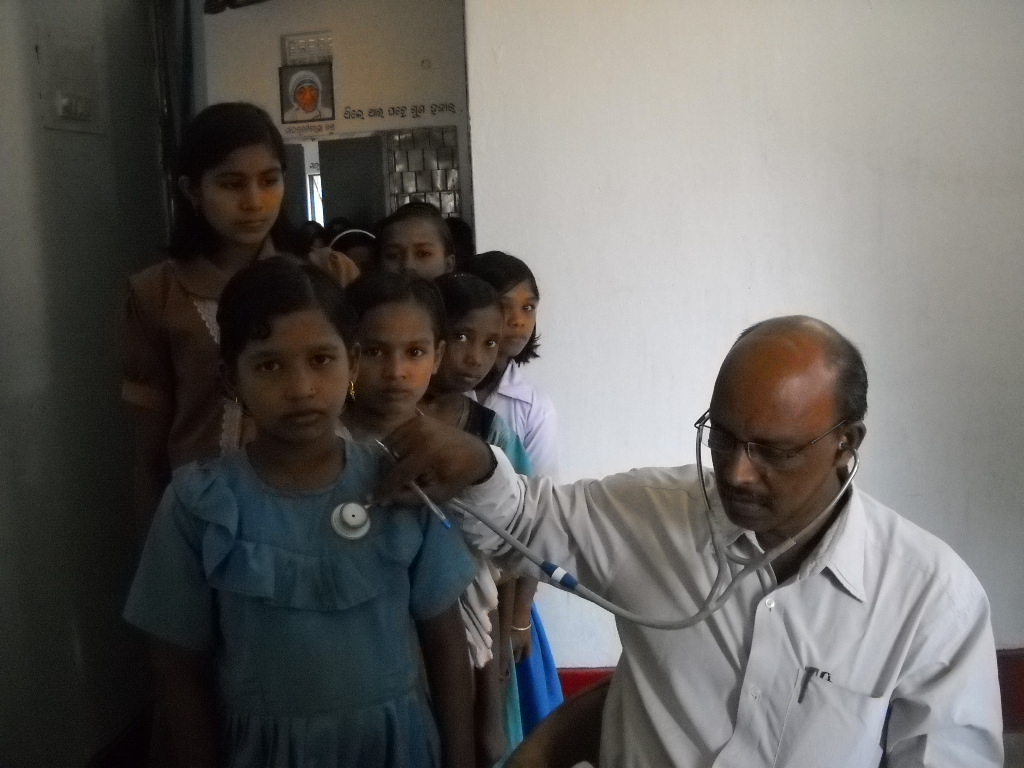
For wellbeing of inmates, regular health check-up is being conducted at the KGBV level in convergence with Chief District Medical Officer & NRHM. In emergency cases inmates are being provided with immediate medical aid. Health Insurance &Health Card has been made for the inmates. First aid is available for emergency and immediate relief. To promote better personal hygiene inmates have been oriented on hygienic practice, menstrual hygiene and they are also encouraged to adopt healthy practice like using of Sanitary Pad. Inmates have been counselled time to time in convergence with W & CD Dept./Guest faculty on Adolescent issues. Besides the above Warden is also maintaining one Health Record Register and one Pad Distribution Register to vigilant over the irregularities during their adolescent period.

To achieve the goals of KGBV scheme & to enrol the most deprived, disadvantaged girls from weaker sections, the strategies are being prepared through meetings, sharing, display of hoarding, publishing advertisement in Newspaper, printing leaflets & other mobilizing activities.
PTA is being organised in each KGBVs for sharing the achievement of the inmates with their parents and to maintain cordial relation for smooth function of the hostel. Further all KGBVs observe Annual Day where the inmates explore their hidden talents. In the said function the students are appreciated for their outstanding achievements in different fields.
The girls enrolled in the KGBVS are mostly dropout for more than a year and even three years in some cases and many girls are at lower learning levels. During first entry to KGBV, a structured assessment is being made to ascertain their level of learning and accordingly they are kept in separate groups. In addition to normal school hour, they also spend an additional 4-5 hour of remedial classes in the morning and evening where appropriate level of content is taught by the part time teachers. Appropriate TLM / TLE have been provided to make the learning process interesting.
KGBVs for special coaching in the Summer. Besides, Life skill education and Art & Craft training have been imparted to make the learning more meaningful and make them self – independent throughout the year.
The following innovative practices are being followed
ANWESHA: An Innovative activity for all round development of the girls in KGBV has been organized on pilot basis in Mayurbhanj district with an objective to explore and encourage the girls , to enhance their self-confidence, etc. about 1758 no of girls participated in the programme. The collector and other district level functionaries participated in the programme.
Physical/ Self-defence Training:To develop physical fitness and enhance the self confidence among the girls, steps taken to provide training. About 18400 no of KGBV girls have already completed the certificate course in Marshal art training during 2018-19. The major objective of the said programme are to build up the self-confidence of the girls to meet any challenges they come across in their day to day life.
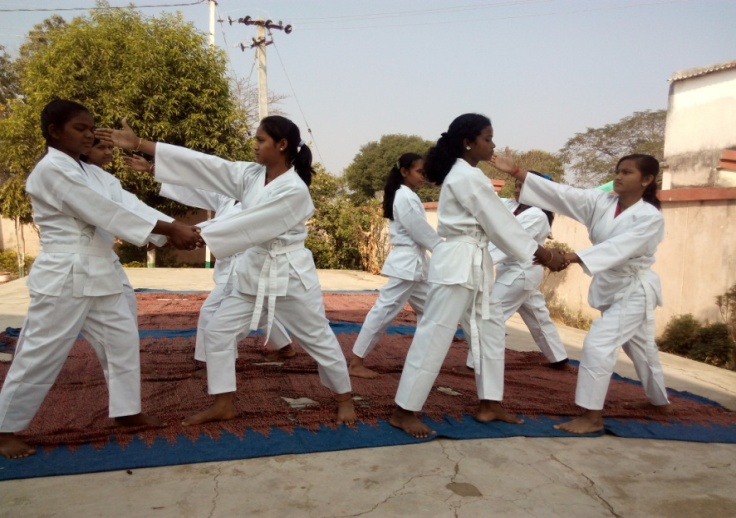
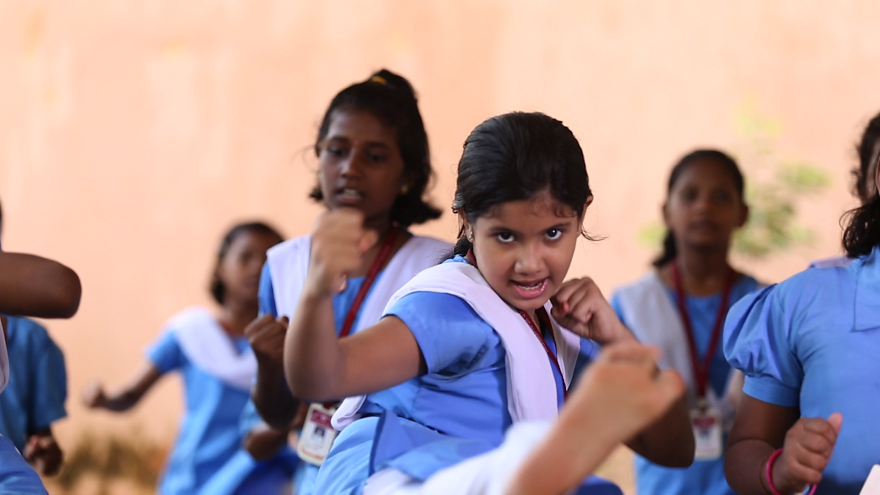



Safety & security of the children is one of the major aspect of healthy school environment for which following measures have been taken in this regard.
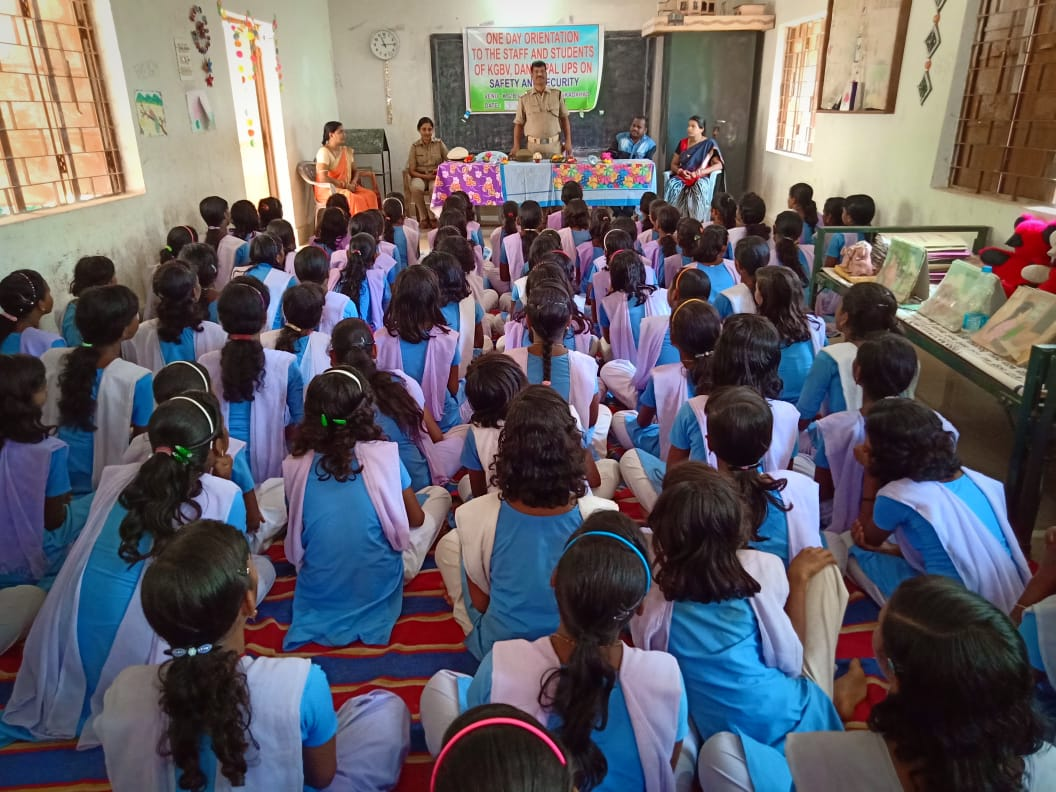

GENDER AND GIRLS EDUCATION
Education is the fundamental right of a child. It is said, “To create a better tomorrow, you must start today with your education which is the only way to success in everyday life as well as in your career”.
Education is the fundamental right of a child. It is said, “To create a better tomorrow, you must start today with your education which is the only way to success in everyday life as well as in your career”. Primary education is the basic necessity of every child and foundation of modern society and of democratic government. Its availability and provision is not only the responsibility of State but also parents and households. Elementary education brings awareness among the masses, opens avenues for opportunities as well self-advancement and reduces chronic and inter-generational poverty. As a first step in the creation of welfare and just society, universal primary/elementary education is an absolute pre-requisite for sustainable development. Girls from disadvantaged communities form the bulk of out-of-school children. The focus in current programmes is to achieve quantitative targets to enable girls to ‘catch up’ with boys. There is need to re conceptualize schematic provisions for gender to ensure that they are cohesive, rather than piecemeal, encompassing all aspects of curriculum, teacher training, peer behaviour as also classroom arrangement.
The issue of ‘hidden curriculum’ in schools will need to be addressed with respect to equity dimensions. Training and academic support will be needed for classroom processes that are gender sensitive, non-discriminatory, free of corporal punishment and mental harassment. Although enrolment of children has been significantly improved but retention still become the issue coupled with achievement level, peer interaction, student teacher relationship in terms of knowledge construction, attitude of community, teachers, free access to school, optimum use of available infrastructure in school in connecting school environment with outside environment, facilitating curricular enhancement by teachers, inculcating democratic values & thoughts among children, community support etc. Children’s voice is not so encouragingly heard to participate in their development process that is the significant indicator of education in learning process. It is the need of the hour to ensure self recognition, self-esteem, self-confidence and self-actualization of children while building of life as a responsible citizen of the society to cater the need of a powerful nation with empowered personalities at different levels. The real empowerment can be achieved when a person irrespective of any gender will express his full potentialities in contributing to the development as a productive member of the society.
The recent enactment of Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act in April-2010, added some provisions that will most significantly impact girl education, in light of some of the barriers that have existed until now in this regard.
| Barriers | RTE Rationale |
|---|---|
| Household/Community Level | A moral responsibility fixed on every parent/guardian to enrol their child in school and ensure to complete the elementary education. |
| School Level Barriers | Barrier free access which overcomes both physical and social factors affecting girls participation in schooling. |
| System Level | RTE mandates the appropriate government and local authorities to provide for children access through opening of schools in inaccessible areas, adequate teaching staff, infrastructure facilities, girl friendly school and classroom environment as well as other entitlements a child required to continue his/her studies in healthy school environment. |
| Policy Level | Every child aged 6 to 14 shall have a right to provision of free Compulsory, equitable quality education. |